Eureka server and Client Communicate
Eureka Server is a service registry provided by Netflix as part of the Spring Cloud ecosystem. It acts as a discovery server where microservices can register themselves and discover other registered services.
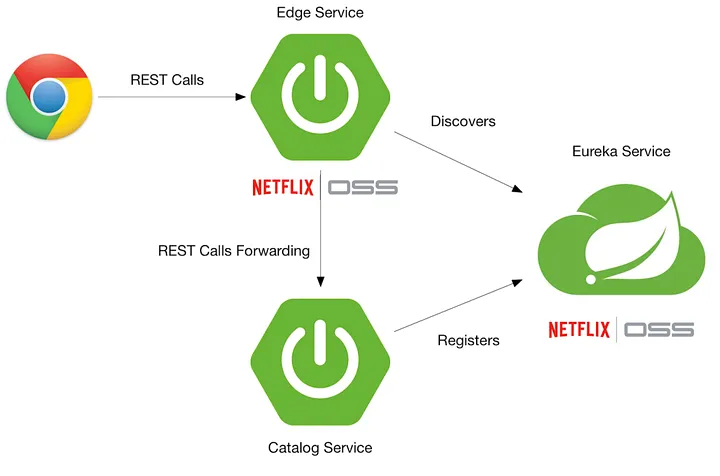
Table of Contents
Eureka Client
Eureka Client is a microservice that registers itself with the Eureka Server. It also retrieves a list of other registered services from the Eureka Server, enabling it to discover and communicate with them.
Communication Process
- 1. Service Registration: When a Eureka client starts, it registers itself with the Eureka server. This involves sending metadata about the service, such as its hostname, port, health indicator URL, and service ID.
- 2. Service Discovery: When a client needs to communicate with another service, it queries the Eureka server to get the location (hostname and port) of the service it wants to communicate with.
- 3. Heartbeat: The client sends periodic heartbeats to the Eureka server to renew its lease and let the server know it’s still active.
- 4. Service De-registration: When a client shuts down, it sends a de-registration request to the Eureka server to remove itself from the registry.
Java Example
Here’s a basic Java example using Spring Boot to demonstrate how Eureka Server and Client communicate.
Step 1: Set up Eureka Server
```xml
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
```
application.properties
```properties
server.port=8761
eureka.client.register-with-eureka=false
eureka.client.fetch-registry=false
```
EurekaServerApplication.java
```java
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaServer
public class EurekaServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EurekaServerApplication.class, args);
}
}
```
Step 2: Set up Eureka Client
```xml
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
```
application.properties
```properties
server.port=8080
eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone=http://localhost:8761/eureka/
spring.application.name=eureka-client
```
EurekaClientApplication.java
```java
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
public class EurekaClientApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EurekaClientApplication.class, args);
}
}
```
Step 3: Service Discovery
```java
@RestController
public class ServiceController {
@Autowired
private DiscoveryClient discoveryClient;
@GetMapping("/services")
public List<String> getServices() {
return discoveryClient.getServices();
}
@GetMapping("/instances/{serviceId}")
public List<ServiceInstance> getServiceInstances(@PathVariable String serviceId) {
return discoveryClient.getInstances(serviceId);
}
}
```
In this setup:
- 1. The Eureka server is set up on port 8761.
- 2. A Eureka client registers itself with the Eureka server.
- 3. The client can discover other services registered with the Eureka server.
