Hibernate Second Level Cache
Explanation
- Definition : The second-level cache in Hibernate is an optional cache that stores objects across sessions. Unlike the first-level cache, which is specific to a session, the second-level cache can be shared among different sessions and is typically used to cache frequently accessed data.
- Scope : The second-level cache spans the entire SessionFactory, meaning it is shared across multiple sessions.
- Configuration : Hibernate supports various caching providers, one of which is EHCache. EHCache is a widely-used, open-source caching library for Java that integrates well with Hibernate.
Advantages
- Improved Performance : By caching objects at the SessionFactory level, it reduces database access for frequently used data, thereby improving performance.
- Reduced Load : It reduces the load on the database, especially for read-heavy applications.
Steps to Configure Hibernate Second Level Cache
- Add Dependencies : Include the necessary Hibernate and EHCache dependencies in your pom.xml or build.gradle file.
- Configure Hibernate : Update the Hibernate configuration file (hibernate.cfg.xml) to enable the second-level cache and specify EHCache as the provider.
- Configure EHCache : Create an ehcache.xml configuration file to define cache regions and settings.
- Annotate Entities : Use Hibernate annotations to specify which entities and collections should be cached.
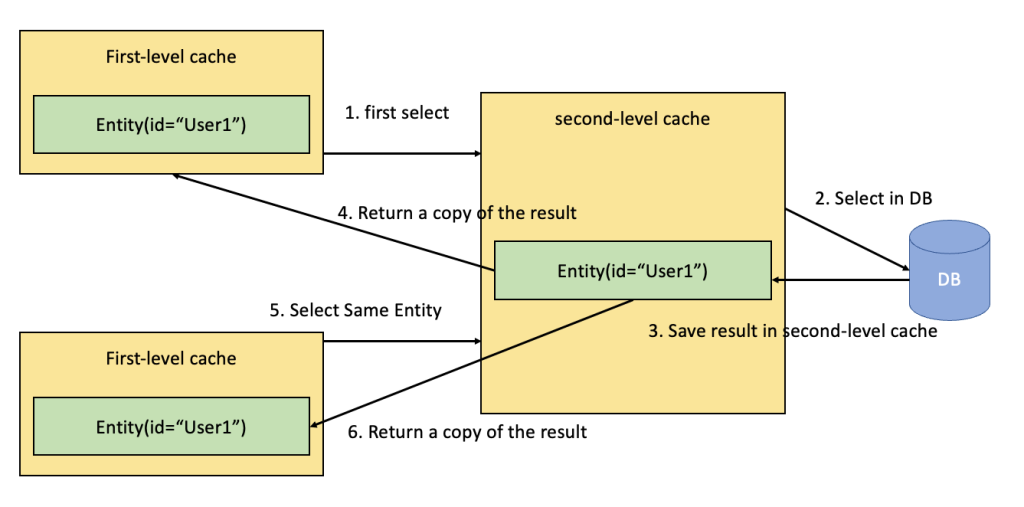
Table of Contents
Step 1: Add Dependencies (Maven Example)
Step 1: Add Dependencies (Maven Example)
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
<version>5.4.32.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-ehcache</artifactId>
<version>5.4.32.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sf.ehcache</groupId>
<artifactId>ehcache</artifactId>
<version>2.10.6</version>
</dependency>
Step 2: Configure Hibernate (hibernate.cfg.xml)
Step 2: Configure Hibernate (hibernate.cfg.xml)
xml
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<!-- Database connection settings -->
<property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/your_database</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.username">your_username</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.password">your_password</property>
<!-- Hibernate properties -->
<property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto">update</property>
<!-- Enable second-level cache -->
<property name="hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache">true</property>
<property name="hibernate.cache.region.factory_class">org.hibernate.cache.ehcache.EhCacheRegionFactory</property>
<property name="hibernate.cache.use_query_cache">true</property>
<!-- Entity classes -->
<mapping class="com.example.Student"/>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
Step 3: Configure EHCache (ehcache.xml)
Step 3: Configure EHCache (ehcache.xml)
xml
<ehcache>
<defaultCache
maxEntriesLocalHeap="10000"
eternal="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="300"
timeToLiveSeconds="600"
overflowToDisk="true"
diskPersistent="false"
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/>
<cache name="com.example.Student"
maxEntriesLocalHeap="1000"
eternal="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="300"
timeToLiveSeconds="600"
overflowToDisk="true"
diskPersistent="false"
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/>
</ehcache>
Step 4: Annotate Entities
Step 4: Annotate Entities
java
import javax.persistence.*;
import org.hibernate.annotations.Cache;
import org.hibernate.annotations.CacheConcurrencyStrategy;
@Entity
@Table(name = "student")
@Cacheable
@Cache(usage = CacheConcurrencyStrategy.READ_WRITE)
public class Student {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "id")
private int id;
@Column(name = "first_name")
private String firstName;
@Column(name = "last_name")
private String lastName;
@Column(name = "email")
private String email;
// Getters and setters
// toString method
}
Example of Hibernate Second Level Cache
In this example, EHCache is configured as the second-level cache provider. The Student entity is marked as cacheable, meaning instances of Student will be stored in the second-level cache according to the settings defined in ehcache.xml.
