Transport layer security for our web apps
Transport Layer Security (TLS) is a protocol that ensures privacy between communicating applications and their users on the internet. When securing a web application with TLS, you encrypt the data exchanged between the client and the server, preventing eavesdropping and tampering. To achieve TLS for your web application, you need to:
1. Obtain an SSL/TLS Certificate
Get a certificate from a trusted Certificate Authority (CA).
2. Configure Your Web Server
Set up your web server (e.g., Apache, Nginx, Tomcat) to use the obtained certificate and enable HTTPS.
3. Enforce HTTPS in Your Application
- Redirect HTTP requests to HTTPS.
- Use secure cookies and headers to ensure all communication is over HTTPS.
4. Test the Configuration
Use online tools to verify the SSL/TLS setup and ensure there are no vulnerabilities.
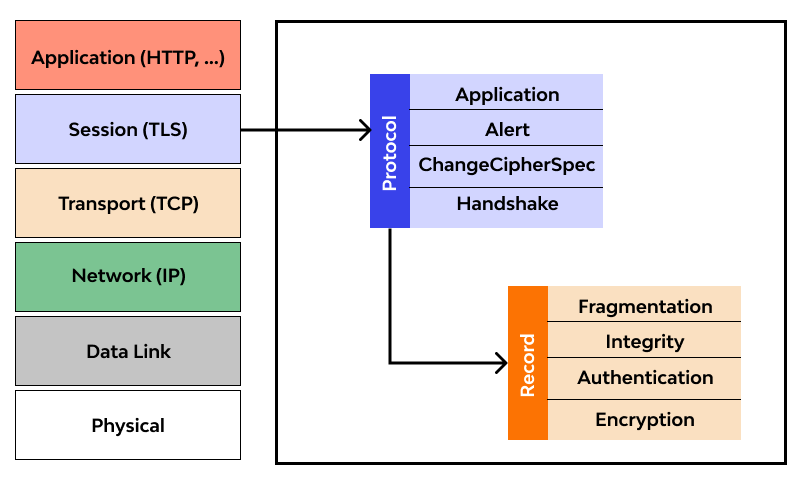
Table of Contents
Java Example
In this example, we’ll configure a Java-based web application running on Apache Tomcat to use TLS.
Obtain an SSL/TLS Certificate
You can obtain an SSL/TLS certificate from a trusted CA like Let’s Encrypt, DigiCert, or GlobalSign. For development purposes, you can create a self-signed certificate.
Configure Apache Tomcat for HTTPS
Add the following configuration to your server.xml file in the Tomcat conf directory:
xml
<Connector port="8443" protocol="org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol"
maxThreads="150" SSLEnabled="true">
<SSLHostConfig>
<Certificate certificateKeyFile="conf/localhost-rsa-key.pem"
certificateFile="conf/localhost-rsa-cert.pem"
type="RSA" />
</SSLHostConfig>
</Connector>
3. Enforce HTTPS in Your Application
You can use a servlet filter to redirect HTTP requests to HTTPS.
java
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.Filter;
import javax.servlet.FilterChain;
import javax.servlet.FilterConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.ServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebFilter;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@WebFilter("/*")
public class HttpsRedirectFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
// Initialization logic, if needed
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest httpRequest = (HttpServletRequest) request;
HttpServletResponse httpResponse = (HttpServletResponse) response;
if (!httpRequest.isSecure()) {
String httpsUrl = "https://" + httpRequest.getServerName()
+ ":8443" + httpRequest.getRequestURI();
if (httpRequest.getQueryString() != null) {
httpsUrl += "?" + httpRequest.getQueryString();
}
httpResponse.sendRedirect(httpsUrl);
return;
}
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
// Cleanup logic, if needed
}
}
Explanation Transport layer
- 1. SSL/TLS Configuration in Tomcat:
- The Connector element is configured to listen on port 8443 for HTTPS connections.
- SSLHostConfig specifies the certificate and key files.
- 2. HttpsRedirectFilter:
- This filter intercepts all incoming requests (/* URL pattern).
- If a request is not secure (!httpRequest.isSecure()), it redirects the request to the HTTPS URL.
- Constructs the HTTPS URL using the server name, port, request URI, and query string.
