Database connection and log4j integration
Integrating database connections and logging using Log4j in a servlet involves configuring a database connection pool, establishing connections in the servlet, and setting up Log4j for logging purposes.
1. Database Connection:
- Use a connection pool (e.g., Apache DBCP or HikariCP) to manage database connections efficiently.
- Configure the connection pool in a configuration file (e.g., context.xml or web.xml).
2. Log4j Integration
- Add Log4j dependencies to the project.
- Configure Log4j using a properties file or XML configuration file (e.g., log4j.properties or log4j.xml).
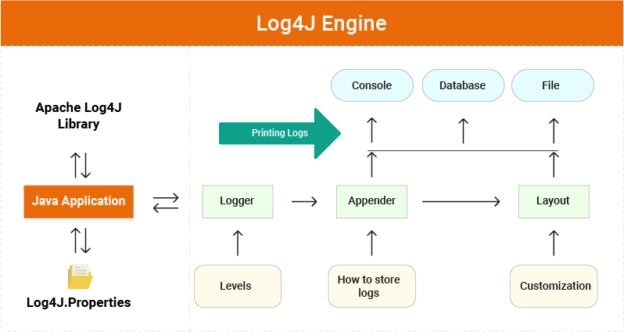
Table of Contents
Add Dependencies
Add dependencies for Log4j and a connection pool library (e.g., Apache DBCP) to your pom.xml (for Maven projects).
Example
xml
<dependencies>
<!-- Log4j dependencies -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-api</artifactId>
<version>2.14.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-core</artifactId>
<version>2.14.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Apache DBCP dependencies -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-dbcp2</artifactId>
<version>2.8.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Configure Database Connection Pool
Create a context.xml file in the META-INF directory to configure the connection pool.
xml
<Context>
<Resource name="jdbc/MyDB"
auth="Container"
type="javax.sql.DataSource"
maxTotal="20"
maxIdle="10"
maxWaitMillis="-1"
username="dbuser"
password="dbpassword"
driverClassName="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"
url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydatabase"/>
</Context>
Configure Log4j
Create a log4j.properties file in the src/main/resources directory.
properties
Define the root logger with appender file
log4j.rootLogger = DEBUG, FILE
Define the file appender
log4j.appender.FILE = org.apache.log4j.FileAppender
log4j.appender.FILE.File = logs/application.log
log4j.appender.FILE.ImmediateFlush = true
log4j.appender.FILE.Threshold = debug
log4j.appender.FILE.Append = true
log4j.appender.FILE.layout = org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.FILE.layout.ConversionPattern = %d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} %-5p %c{1}:%L - %m%n
Example
Step 4: Implement the Servlet
Here is an example servlet that demonstrates how to use database connections and Log4j logging:
java
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import javax.naming.Context;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.apache.logging.log4j.LogManager;
import org.apache.logging.log4j.Logger;
@WebServlet("/DatabaseServlet")
public class DatabaseServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private static final Logger logger = LogManager.getLogger(DatabaseServlet.class);
private DataSource dataSource;
public void init() throws ServletException {
try {
Context initContext = new InitialContext();
Context envContext = (Context) initContext.lookup("java:/comp/env");
dataSource = (DataSource) envContext.lookup("jdbc/MyDB");
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Failed to initialize DataSource", e);
throw new ServletException("Cannot initialize DataSource", e);
}
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = dataSource.getConnection();
String sql = "SELECT * FROM mytable";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
out.println("<html><body>");
out.println("<h1>Database Results</h1>");
out.println("<table border='1'><tr><th>ID</th><th>Name</th></tr>");
while (resultSet.next()) {
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String name = resultSet.getString("name");
out.println("<tr><td>" + id + "</td><td>" + name + "</td></tr>");
}
out.println("</table></body></html>");
logger.info("Data retrieved successfully from the database.");
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Database connection or query failed", e);
out.println("Error retrieving data from the database.");
} finally {
try {
if (resultSet != null) resultSet.close();
if (statement != null) statement.close();
if (connection != null) connection.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Failed to close database resources", e);
}
}
out.close();
}
}
Explanation Database connection and log4j integration
- Database Configuration:
- context.xml defines the database connection pool parameters, including the database URL, credentials, and connection pool properties.
- Log4j Configuration:
- log4j.properties sets up the logging level, log file location, and log message format.
- Servlet Implementation:
- init() method initializes the DataSource by looking it up in the JNDI context.
- doGet() method obtains a connection from the connection pool, executes a query, and logs the process using Log4j.
- Logging:
- Log messages are generated using Log4j for successful data retrieval and error conditions.
